
This includes the activity of the accessory male sex organs and development of male secondary sex characteristics. The androgens stimulate and control the development and maintenance of male characteristics (and of female characteristics to lesser extend). However, when secreted they are transported to the gonads either testes or ovaries where they are converted to the more potent testosterone and to the most potent sex steroid hormone called dihydrotestosterone. The zona reticularis secretes androstenedione, dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrostenedione which are not effective androgens as testosterone.


The cortical zonae are the zona glomerulosa, fasciculata and reticularis producing and secreting minerocorticoids, glucocorticoids and sex steroids respectively. The adrenal cortex composes the outer layer of the adrenal gland and consists of three sublayers called zonae each of which produces structurally similar and functionally different compounds and hormones. The adrenal gland divides into the adrenal outer cortex and the adrenal inner medulla with the latter being of neuronal embryonic origin.
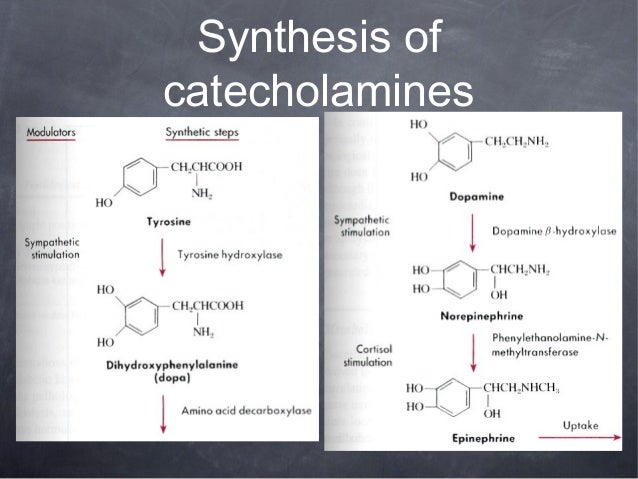
They have many activities due to their dual embryonic origin during development.

The adrenal glands or suprarenal glands are small paired organs situated superiorly to the kidneys resembling caps surrounded by dense adipose tissue.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
